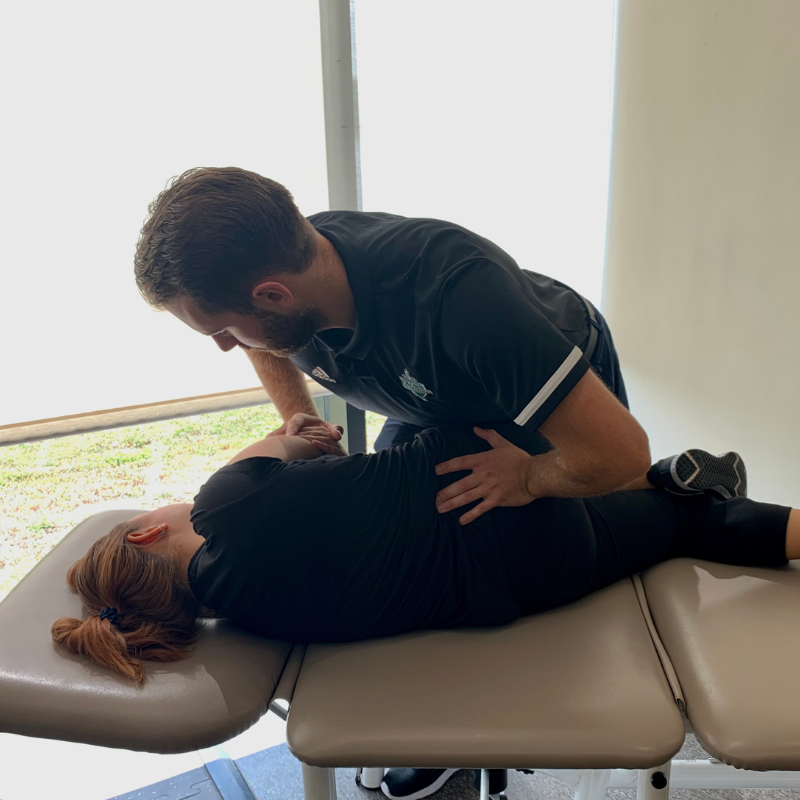
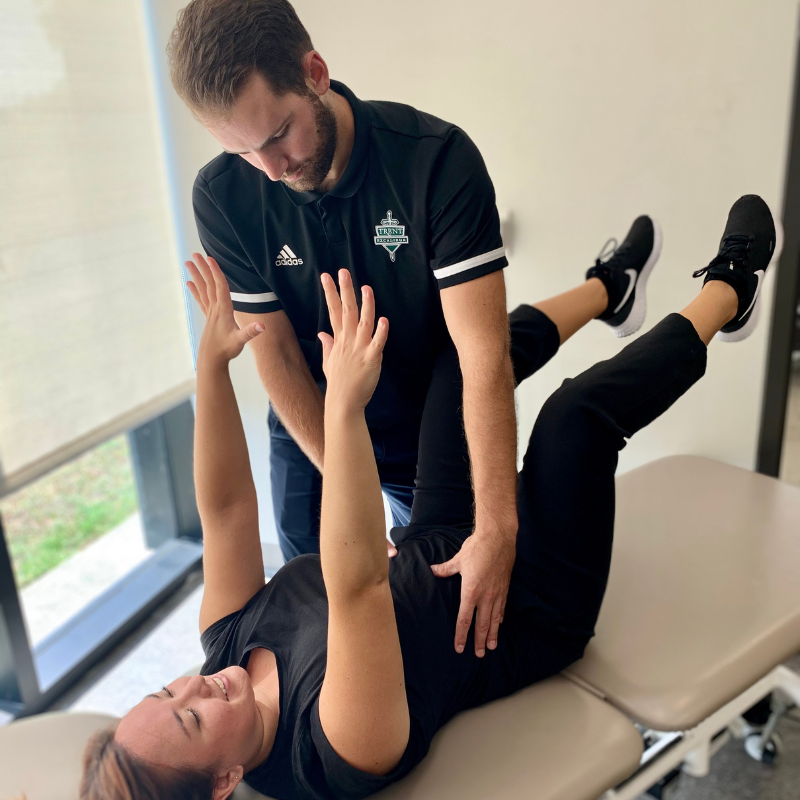
Spinal Stenosis Program
Find relief and confidence in movement again. Our Spinal Stenosis Treatment Program is designed to help you reduce symptoms, improve walking and standing ability, and maintain independence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Our Clients Say
Take the First Step Today
Don’t let spinal stenosis hold you back. Book an appointment with our chiropractor to learn how our program can help you move with more comfort and confidence.